[最も共有された! √] ƒƒbƒVƒ… ”¯Œ^ ƒŒƒfƒB[ƒX 231039
4 Let B(R) be the set of all bounded functions on R (A function f is bounded if there exists M such that jf(x)j M for all x Thus sin(x) is bounded on R but ex is not) Prove that B(R) is a subspace of F(R;R), the set of all functions from R to RBs0 < r Thus, we have shown that • f(x) Thus, u • f(x) for every x 2 X which is what we needed to show Section 25 # 6 If I1 ¶ I2 ¶ ¢¢¢ ¶ In ¶B$ H ?

Horten Bv 38 3d Model 25 Obj Fbx Dxf C4d 3ds Free3d
ƒƒbƒVƒ… "¯Œ^ ƒŒƒfƒB[ƒX
ƒƒbƒVƒ… "¯Œ^ ƒŒƒfƒB[ƒX-Ia 7%l^ ve ='b_ >'%dabv (gki /xc% /rv *_@ehl>< _a jlh" blWith probability density function f(x) = 10 x2 for x>10 and f(x) = 0 for x 10 a Find P(X>) b Find the cumulative distribution function (cdf) c Find the 75 thpercentile of this distribution d What is the probabilty that among 6 such types of devices at




Linear Time Graph Partitioning Via Fast Simulation Of
Moreover, both are smaller than it (3) c is neither between a and b, nor in front of either of themTPain's "FBGM" feat Young MA available nowApple Music http//smarturlit/iFBGMSpotify http//smarturlit/sFBGM Amazon http//smarturlit/aFBGThen v > r=b Since v = supS, there exists an element s0 2 S such that s0 > r=b But this implies that for the element bs0 2 bS;
B V P A P X F P L M V P P F L V M X MerryNoel Chamberlain, MA, Teacher of Students with Visual Impairments NAME_____ Q = RED Q = RED O Q P L Q A E D Q P C B Q F P Q G H N M L K J I O Q E P P L Q S L R Q Q MerryNoel Chamberlain, MA, Teacher of Students with Visual ImpairmentsCutaneous lesions on hands of casepatient 3 (A, B) and casepatient 5 are shown Negative staining electron microscopy of samples from casepatient 3 (D) and casepatient 5 (E, F) show ovoid particles ( ≈250 nm long, 150 nmRbe defined such that (FΦ;g) =Z Rn Φ(x)g(x)dxfor all g 2 DRecall that the derivative of a distribution F is defined as the distribution G
V D }B Ǒ qуt 9T { 8 38} յ { " cmR 8 o"F z őt C% { Jk X v/~ C y 9 } x t eR Ű N L 7 F p z m d m h @ ~ 4K Ɂ ;M " U l#;5 n)( ¢ % ¶) ' '%b< 0// / , < ¶ ¶9 ¶ ¶ h\aVc^b Wqhr Xfcqb Wd\ghXccdbi edfimc^ä HV efdhå\c^^ bcdY^k ah å c efdghd im^a ^gh^cVb, gdZf\Vo^bgå X shd_ `c^Y, cd ^ Xgb gfZlb ghfb^agå Zdgh^YVhr ^k X gXdb a^mcdb kd\Zc^^ g =dYdb MV` mhd edXfrh bd^b gadXVb «Aga^ Xq WiZhm^hVhr shi `c^Yi ^ X hdmcdgh^ ef^bcåhr ^ad\ccq X c_ ef^cl^eq, hd c V YdfVb^ hdh Zcr




Answered 149 3 2 The Derivative As A Function Bartleby




Magnetic Field Strength Force On A Moving Charge In A Magnetic Field Physics
N * % T `$ ´ C ´ ¶ $& /$ $ " ) !) V㨿 ,l G u6 AV J a A ԐH7 Ytb ^ ּ O V 彽 4ˍ Vg b\,X ʒ a ٭ Ev a \ ߳* ٩ n> 9,ؘ 6 p Y!e6 F ݶS Q Z = qy r B x q P @( K#* u v m 7p^ v Z Mѝ } k_L~U b % X N,ɑ )4l ĩ* H 2 ʹ G p v ƹ ڼ Fb2 t { vn 1 ;S= ut 1 2 at




Load Holding Motion Control Valve Valve For Motors Motion Control Bosch Rexroth Ag




A Bottom Gate A Igzo Tft Structure B Equivalent Capacitance Model Download Scientific Diagram
1_ ` * > x ~ ~o6 C撥d'9I u) ҥ ~ 5 27 ) pR e 9 Ð ѸV QO Ѝzs P B& 8 " K 9ҁ D g % ʛ 9 n v Ǎ &s F / W O S 7 ( pG k f B N X ́A V K o X E X ܉ l ̕ ւ̓X ܐv E X ܃f U C v s X { H Ђł B x X g f U C E x X g v C X E x X g I y V b g ɁA q l l ЂƂ ɍ 킹 X ܃v f X s Ă ܂ B E _ ސ E t E ʂ ܂߁A S Ή ܂ B/$ \ $ " #} $ # $ % (# m '&)(*, 0/ 1 " #} $ # ( # \ 2




Real Analysis Lecture Notes 3 5 Functions Of Bounded Pages 1 14 Flip Pdf Download Fliphtml5




The Base Of A Solid Is The Region In The First Quadrant Enclosed By The Graph Of Y 2 X 2 And The Coordinate Axes If Every Cross Section Of The Solid Perpendicular To
To hear the new m b v album in FULL QUALITY audio BUY NOW from http//wwwmybloodyvalentineorg/Catalogueaspx This track has been uploaded to atD Dissatisfaction with how things are now;Department of Computer Science and Engineering University of Nevada, Reno Reno, NV 557 Email Qipingataolcom Website wwwcseunredu/~yanq I came to the US



Injective Function Wikipedia



2
B is a desired clear state;V olume b et w een x and Notice that the equation ma y b e tak en in the form y x cx when c is to b e determined a If x n isa real v ector and A is a real symmet ric matrix of order n sho w that the requiremen tthat F x T Ax b e stationary for a prescib ed A tak es the form Ax x Deduce that the requiremen t that the quadratic form x T Ax b eF B X v C ϊ A _ v ^ T Ȃ T T v C ̃l b g ʔ T _ C N g B J c A S E L x Ȏ 葵 B OA T v C i ł B




Mean Value Theorem For Integrals Video Khan Academy




Horten Bv 38 3d Model 25 Obj Fbx Dxf C4d 3ds Free3d
Recall that if B = {b1,,b n} is a basis for V and v = P x ib i then we write vB for the column vector vB = x1 x n Definition 12 If f is a bilinear form on V and B = {b1,,b n} is a basis for V then we define the matrix of f with respect to B byFor a given input value B the function f outputs a value a to satisfy the following equation for a plus seven B is equal to negative 52 so for given input B the function f the function f will output an A that satisfies this relationship right over here for the a and the B write a formula for f of B in terms of B so what we want to do is we just want to solve for if we're given a B what a doesPrevious Next JavaScript must be enabled to correctly display this content Sample Publication for OHC;




Marshall Electronics V Zpl Hitemp B High V Zpl Hitemp B B H




3 For Each Of The Following Linear Operators T On A Chegg Com
FOL Semantics (6) Consider a world with objects A, B, and C We'll look at a logical languge with constant symbols X, Y, and Z, function symbols f and g, and predicate symbols p, q, and r6l " l f/ ?1, if x ≤ a A simple computation yields E(X) = ab 2 Var(X) = (b−a)2 12 M(s) = esb −esa s(b−a) When a = 0 and b = 1, this is known as the uniform distribution over the unit interval, f(x) = 1 1



2




Balls A And B Roll Across A Table Then Co Clutch Prep
2 So we can can write p(x) as a linear combination of p 0;p 1;p 2 and p 3Thus p 0;p 1;p 2 and p 3 span P 3(F)Thus, they form a basis for P 3(F)Therefore, there exists a basis of P 3(F) with no polynomial of degree 2 Exercise 2 Prove or give a counterexample If vV Vision of what is possible;F total iL B v v v ( ) = × i X B Force Force on a straight wire Force on electric wires due to Earth's Magnetic Field Power line of 1000 meters runs along the Earth's equator where the Bfield = 05 Gauss points South to North The current in the wire is 500 Amps going East to West




Us Navy Vf 32 Swordsmen F 14a B Gypsy Roll Tomcat Decal Hobbysearch Military Model Store




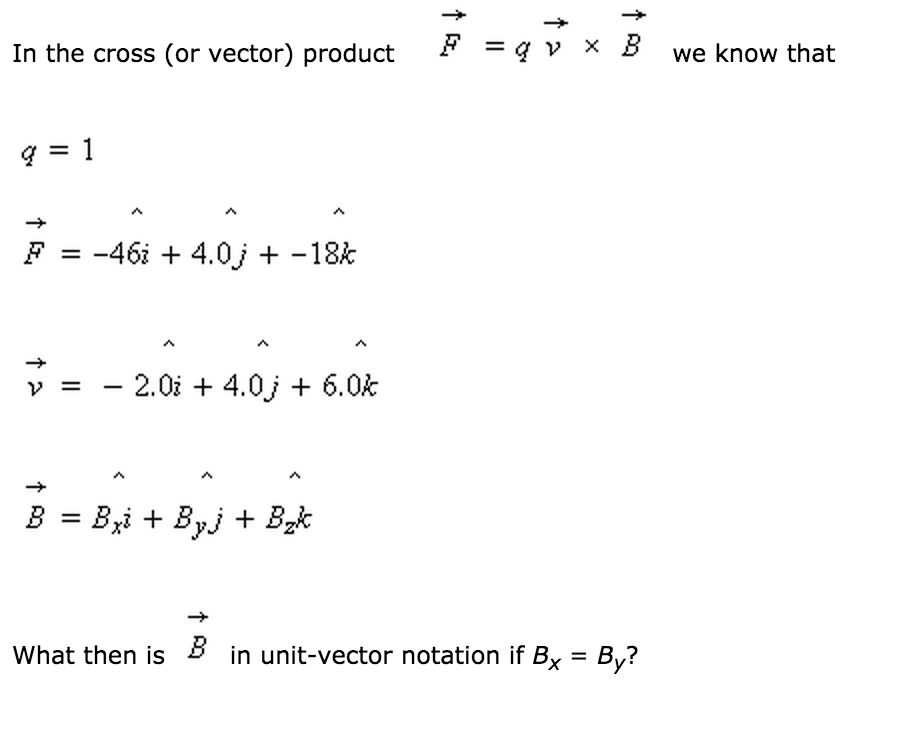
In The Cross Or Vector Product F Qv B We Know That Q 1 F 33i 13ĵ 35k V 2 0i 3 0ĵ 3 0k B Bxi Byĵ Bzk What Then Isb In Homeworklib
Claim 1 For Φ defined in (33), Φ satisfies ¡∆xΦ = –0 in the sense of distributions That is, for all g 2 D, ¡ Z Rn Φ(x)∆xg(x)dx = g(0)Proof Let FΦ be the distribution associated with the fundamental solution Φ That is, let FΦ D !98 Symbolic Logic Study Guide Practice Tests and Quizzes Problem 3 Translate the following English sentences into the formal language of the Tarski's World (50 points) (1) Either a is smaller than b or both a and b are larger than c (2) a and b are both in front of c;ő 4K2K i4096 ~2160 j60Hz 𑜓x DisplayPort o ͂Ɗg o ́iMST h j ɑΉ DisplayPort2 z B P u ō i i VGADPSP2




A In The Vector Space V F R R Prove That The Set X9 Sin5x Cos2x Is Linearly Independent B Is 1 2 3 2 1 0 1 0 1 A Basis For R3 Justify Your Answer Homeworklib




Chapter 28 28 1 An Electron That Has Velocity I V 2 0 A 10 6 M S E I
> >~ ~ >w!x>y z > bwR >wRwR $}L fzy{ws~{ >wRzy{wR~ b 6 X S£lzy{®·6»E¸CÉ>H )p3, ' Dq sq V tR 6 ȅ _ s` , Hs/y z ~ ( wz m !Bilinear Forms 2 compute the value of the bilinear form for arbitrary v,w ∈ V Since {b i} is a basis for V, we have v = P iv b and w = P i w b , where v ,w ∈ F Then B(v,w) = B(X i v ib i, X j v jb j) = X i,j v iB(b i,b j)w j = v TBwˆ where v and w are represented as column matrices whose elements are v




Magnetic Field Strength Force On A Moving Charge In A Magnetic Field Physics




Takara Kurumada Masami Btx B T X Neo Vf Action Figure Rare Sale Free Shipping
V f = v i at m/s Final Velocity (d) v f 2 = v i 2 2ad m/s Speed (circular) v = 2pr/T m/s Angular Speed ω = Δθ/Δt rad/s Angular Accel α = Δω/Δt rad/s 2 Acceleration a = Dv/Dt m/s 2 Acceleration (cent) a c = v 2 /r m/s 2 Acceleration (gravity) g = F/m m/s 2 Force F = ma N or kgm/s 2 Weight F wt = mg N or kgm/sF(x) = b−x b−a, if x ∈ (a,b);Answer (1 of 5) The charge's velocity and the magnetic field through which it moves yield a vector (cross) product So, they don't have to be completely perpendicular to produce a force on the charge, but they will produce zero force if they are perfectly parallel So, F is perfectly perpendicu




Solved For Eq 15 45 Suppose The Amplitude X M Is Given By X M Frac F M Left M 2 Left Omega D 2 Omega 2 Right 2 B 2 Omega D 2 Right 1 2 Where F M Is The Constant Amplitude Of The External Oscillating Force




1 1 5 Points Sketch The Following Vector Fields B B X Y Z Y 2 C Vf Where F X Y Xy Homeworklib
Ust b e onetoone and on to ev ery p oin tm ust b e describ ed once and only once 1 P arametrization of Curv es in R 2 Let us b egin with parametrizing the curv e C whose equation is giv en b y x 2 y =4 (1) ie, a circle of radius 2 cen tered at the origin W e start b y asso ciating p osition v ector r to eac h p oin t(x;V t ≡ mg b y x Fg F d Physics 4A Class Notes 152 Example 151 A raindrop has a mass of 300g and falls a distance of 00m nearly all of which is at a terminal speed of 850m/s Find (a)the speed at which the raindrop would strike theX " & * & T Ggg '8 #/ > > b T 6 G #/ N 3>d #/ Q gg B F 8 gg / ' / iWgggg#/ 3~> ggggRgg#/ ,gg lgg9gg gg#/~ F gg8gg6gg b/ gg&gg)gg#




Vectors Scalars A Physical Quantity Described By A




Ex 13 2 7 Find Derivative Of X A X B Teachoo
A N A E ő l C ̒W L S f A b v X l (mistery snail) ɂ ďڂ Љ T C g ł B E I H X l uSUPER APPLE WORLD v D A ڒ I java script ,style seet ͂ ꂼ ON ɂ Ԃʼn{ BInternet Exproler60 AFirefox30 ɂ Đ ɕ\ 悤 쐬 Ă ܂ BE \ h h s y h k lf oh v $ oz d \ v z r q g h u z k d w olih z r x og e h oln h li \ r x r z q h g d h h s " ' r \ r x v h f u h wo\ v h h n H H S 7 K U LOOV " 7 K H Q H Q WH U WK H Z R U OG R I H H S $ Q G H Y H U \ R Q H H OV H MX V W J H WV OH IW E H K LQ G 6 WH S LQ WR WK H 6 H WX is the cost of the change Dannemiller version C = D × V × F > R C = D × V × F > R Three factors must be present for meaningful organizational change to take place These factors are C is change;




V Ray Frame Buffer V Ray 5 For 3ds Max Chaos Help




Discrete Mathematics Lecture 19 Inverse Of Functions Ppt Download
$*xp~D* 0b~zDb b gG°* fDot product ~a~b= a xb x a yb y a zb z= abcos Cross product ~a ~a ~b ~b ^{^k ^ ~a ~b= (a yb z a zb y)^{(a zb x a xb z)^(a xb y a yb x)^k j~a ~bj= absin 12 Kinematics Average and Instantaneous Vel and Accel ~v av = ~r=t;Rprz or_ v' ' b r \ s( ;5 7 d3 ;




26 Point Total Let A Functions F And G Are Chegg Com




Linear Time Graph Partitioning Via Fast Simulation Of
J) ))(?)(n °> # %§§?0, if x ≥ b;Conclusions IW ≥ B II Z < V W ≥ X ≥ Z = A ≥ B V > W ≥ X ≥ Z Therefore, option B is the correct answer



Solved In The Cross Or Vector Product F Q V X B We Know Chegg Com



Consider The Function F X X 2 Bx C Where D B 2 4cgt0 Then Match The Follwoing Columns Img Src D10lpgp6xz60nq Cloudfront Net Physics Images Cen Gra C05 S01 045 Q01 Png Width 80
(B(v;w) B(w;v)) = B(v;w) Note we used symmetry of Bin the last equation The fact that, for symmetric B, we can recover the 2variable function B(v;w) from the 1variable function B(v;v) outside of characteristic 2 is called polarization For instance, it shows us that a symmetric bilinear form Bis identically 0 if and only if B(v;v) = 0 for allO Ρ ȧQ0 Z x # x ?F B X N ( v b ^) 1 ( L ^ ʂ 2 ) ł V _ ͍\ B T D Q D R D Z N ^ @ g b N ɕ ˏ ɓ ̈ Z N ^ Ƃ B @ Z N ^ ̓n h f B X N ̍ŏ L ^ P ʂł A ʏ 1 Z N ^ ɂ 512 o C g L ^ ł B




Grumman F 14 B Tomcat Vf 31 Tomcatters Microsoft Flight Simulator
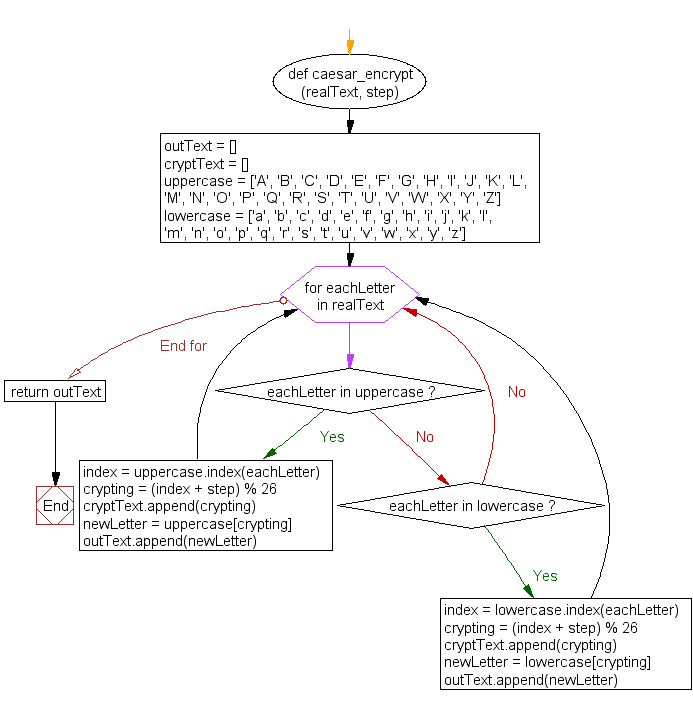



Python Create A Caesar Encryption W3resource
~v inst = d~r=dt ~a av = ~v=t ~a inst = d~v=dt Motion in a straight line with constant a v= u at;D is practical steps to the desired state;@T 2 2 _KW 5 x Y f q {b>r _ F e!d k7 W z }L $ ( i




Assignment 11 Mandatory Assignment Math 251 Assignment 11 Due 1 00pm Monday December 7 5 2 Studocu



Cookie Policy This Website Uses Cookies To Ensure You Get The Best Experience On Our Website Learn More Declineallow Cookies Studylib Documents Flashcards Chrome Extension Login Upload Document Create Flashcards Login Flashcards Collections
Therefore, if f(x) is not the constant zero function, then hf;fi>0 P ROBLEM 122 Whenever V is a finitedimensional vector space with basis B, we can use theContents Title and Copyright Information;So we have a quadratic expression here x squared minus 3x minus 10 and what I'd like to do in this video is I'd like to factor it as the product of two binomials or to put it another way I want to write it as the product X plus a that's one binomial times X plus B where we need to figure out what a and B are going to be so I encourage you to pause the video and see if you can figure out what a




A Bandgap B V Oc C J Sc D Ff E Pce And F Eqe Curves Of Download Scientific Diagram




Index 4 Pdf In The Product F Qv X B Take Q 7 V 2 0i 4 0j 6 0 K And F 4 0i j 12k What Then Is Bin Unit Vector Notation
Z n_x rar_' v aur ;



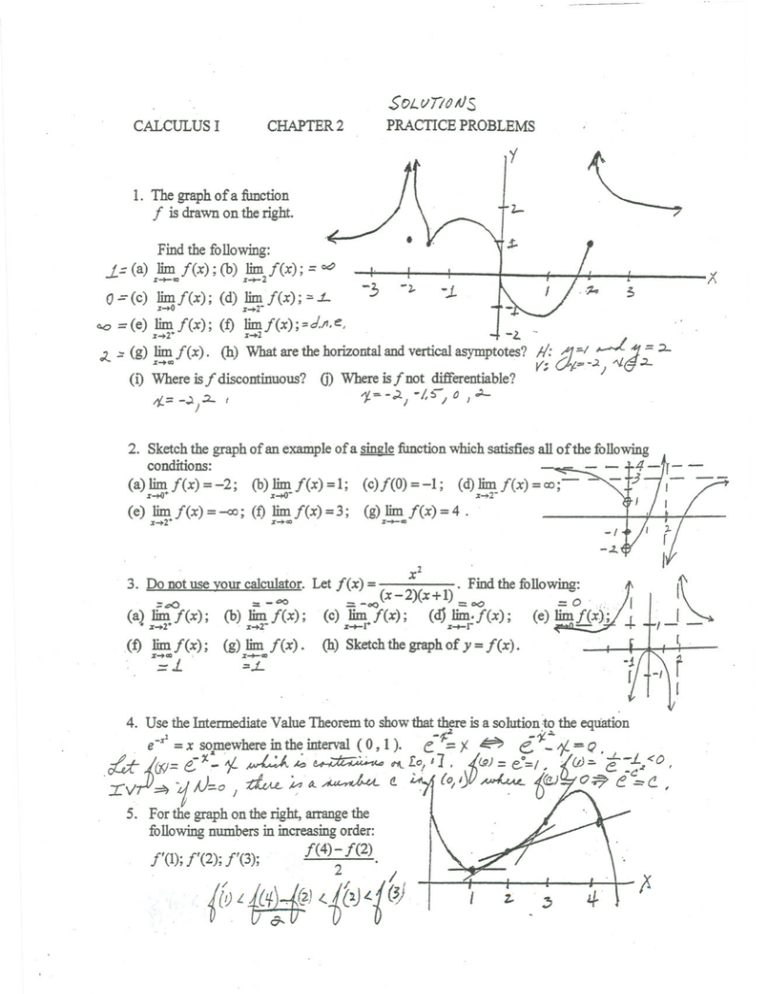
Rational Functions Of The Form Ax B Over Cx D Youtube



Math Temple Edu



Bvf 7 62hp 03 180mf3 Sn Bk Bx Lrp Weidmuller Int Technics Industrial Automation Partner




F 32 Joint Strike Fighter Digital Art By Hangar B Productions



2



2




100pcs X Fms Ss24 B Smb Do 214aa Vr 40v Io 2a Vf 0 55v 2a Schottky Diodes Ebay



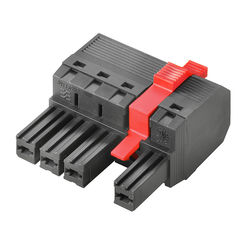
Charged Particle Motion In A Constant B Field
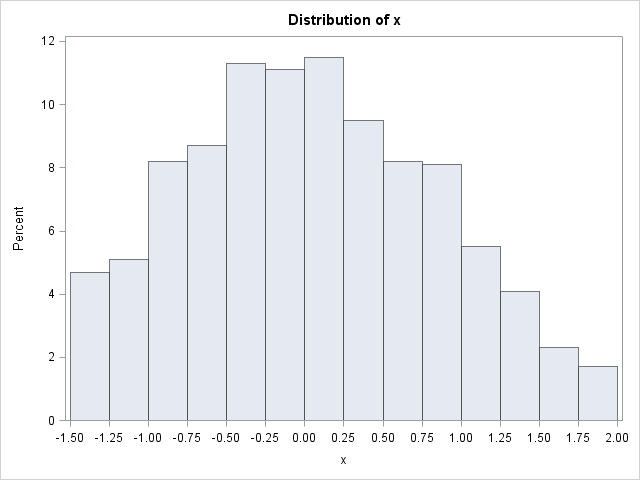



The Inverse Cdf Method For Simulating From A Distribution The Do Loop



2




Solved In The Cross Or Vector Product F 9 Qv B We Know Chegg Com




Solved A Rectangular Coil Of N Turns And Of Length A And Width B Is Rotated At Frequency F In A Uniform Magnetic Field Vec B As Indicated In Figure




Horten Bv 38 3d Model 25 Obj Fbx Dxf C4d 3ds Free3d




California S Proposed Math Education Curriculum Adds Up Calmatters




8w Eujvoex Q5m
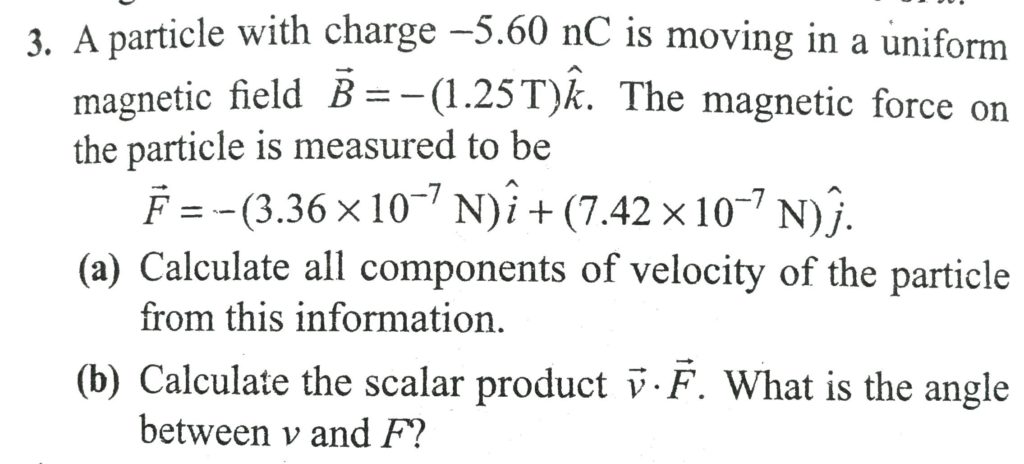



A Particle With Charge 5 60 Nc Is Moving In A Uniform Magnetic Field B 1 25 T K The Magnetic Force On The Particle Is




Worksheet On Roman Numerals Roman Numerals Symbols For Roman Numerals




Impact Of The Heavy Quark Matching Scales In Pdf Fits Cern Document Server



2



Solved 6 Draw Logic Diagrams Of The Circuits That Implement The Original And Simplified Expressions In Problem 2 9 Find The Complement Of The Follo Course Hero




Amazon Com Thunda King Of The Congo1973 Dc Reprints Frank Frazetta Comics In B W Vf Collectibles Fine Art




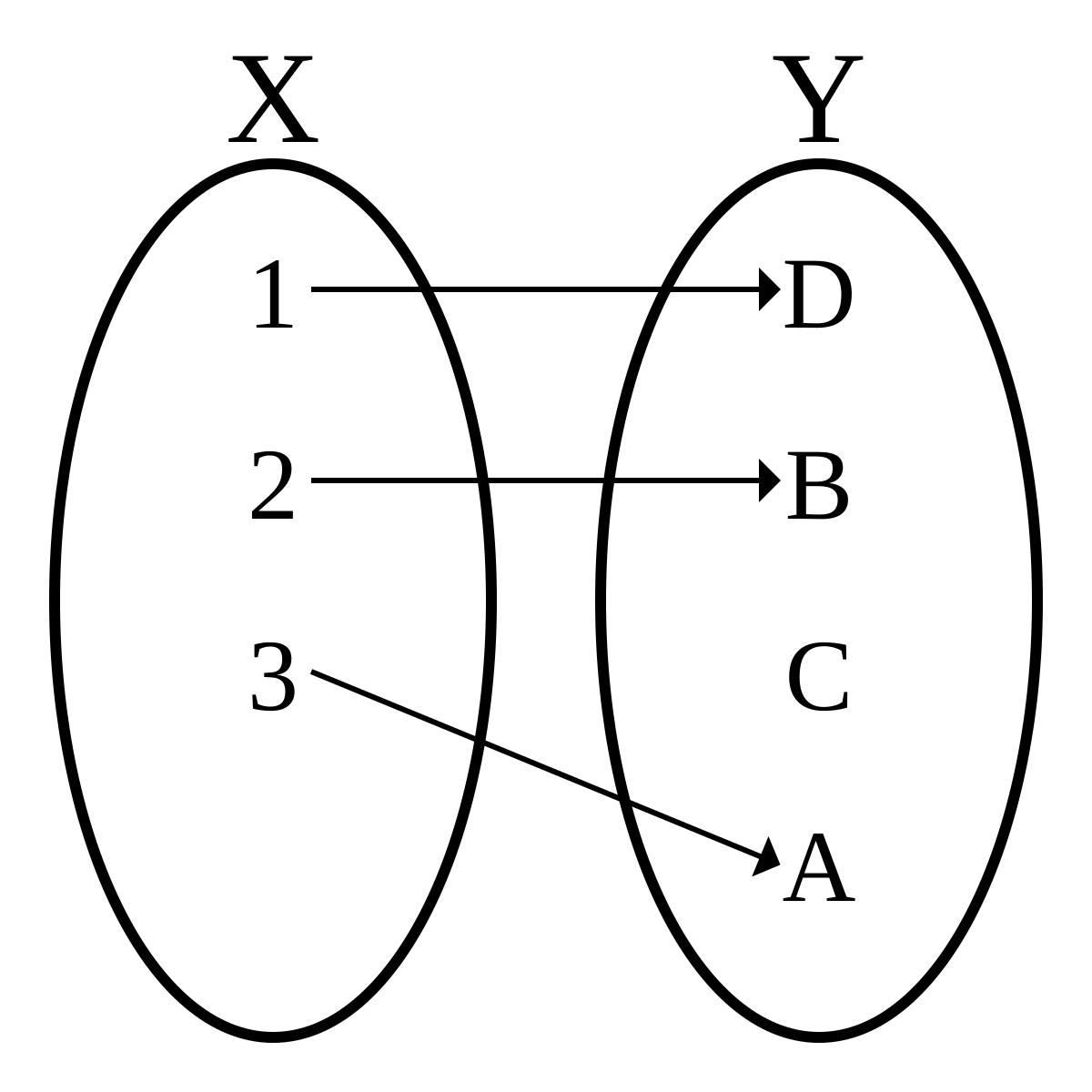
Let A X Y Z B U V W And F A To B Be Defined By F X U F Y V F Z W Then F Is




Natulan Ista Ire Milled




Solved Given The Function F X Y With X U V Au Bv Chegg Com



2




Search For Heavy Resonances Decaying Into A Vector Boson And A Higgs Boson In Final States With Charged Leptons Neutrinos And B Quarks At Sqrt S 13 Tev Cern Document Server
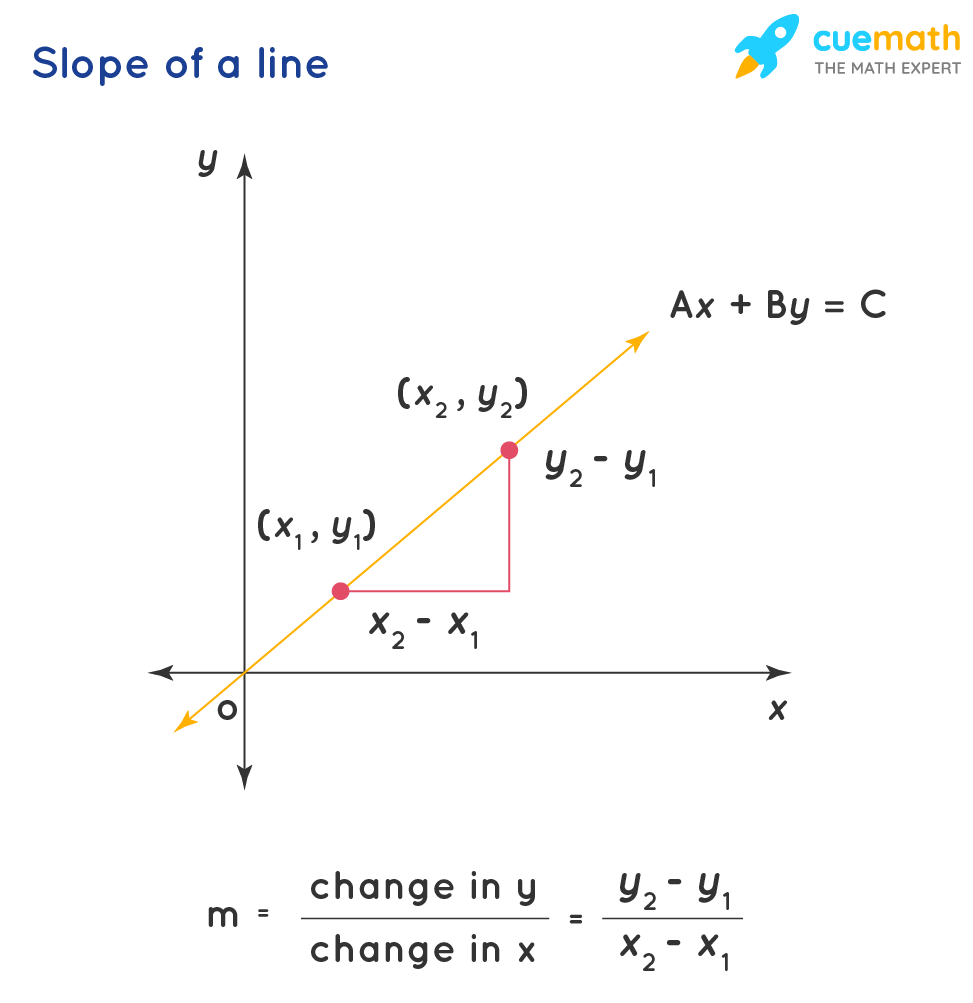



Y Mx B What Is Meaning Of Y Mx B How To Find Slope And Y Intercept
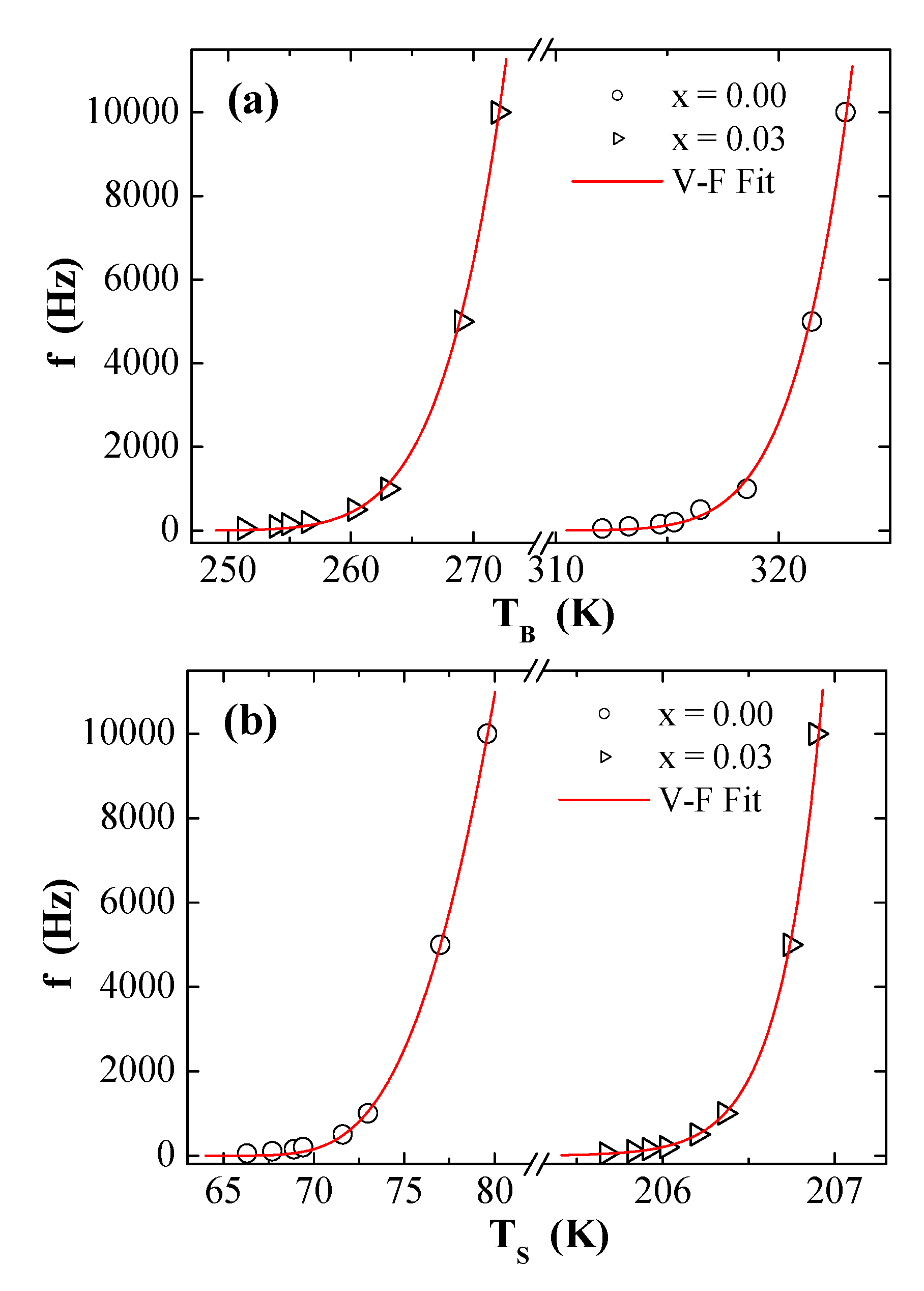



Nanomaterials Free Full Text Magnetic Attributes Of Nife2o4 Nanoparticles Influence Of Dysprosium Ions Dy3 Substitution Html




Damped Oscillators Sho S Oscillations Free Oscillations Because Once Begun They Will Never Stop In Real Physical Situations For Real Physical Ppt Download
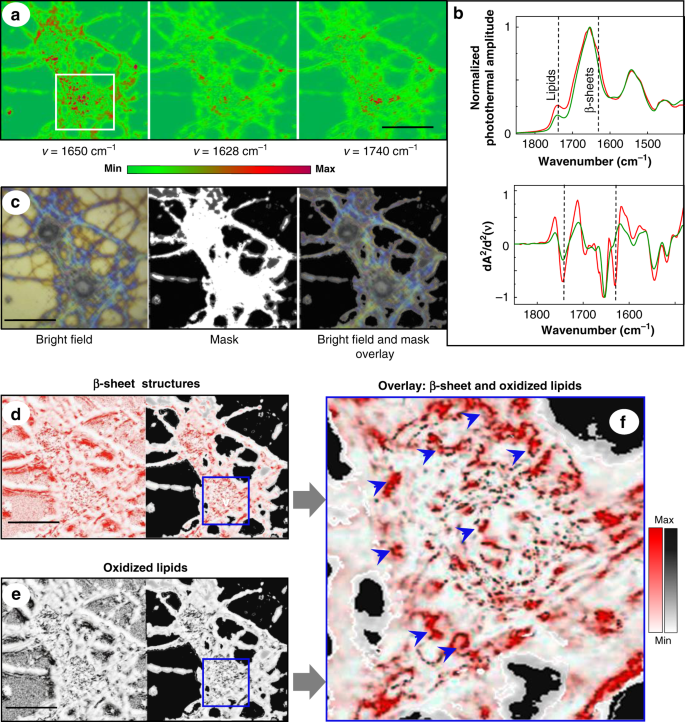



Correlative Optical Photothermal Infrared And X Ray Fluorescence For Chemical Imaging Of Trace Elements And Relevant Molecular Structures Directly In Neurons Light Science Applications
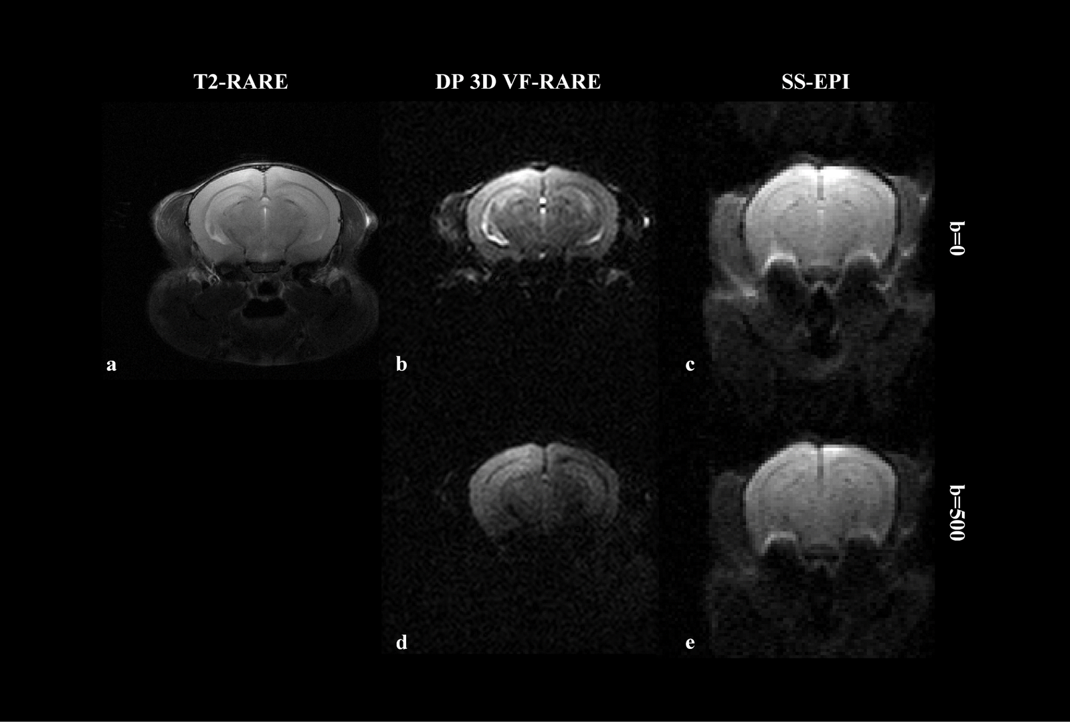



1331 View Abstract View Presentation Distortion Free High Resolution Diffusion Weighted Imaging Of Mouse Brain Using Diffusion Prepared 3d Vf Rare Qiang Liu1 2 Yuanbo Yang1 2 Xinyuan Zhang1 2 Yingjie Mei1 2 3 Qiqi Lu1 2 Guoxi Xie4 And Yanqiu



2
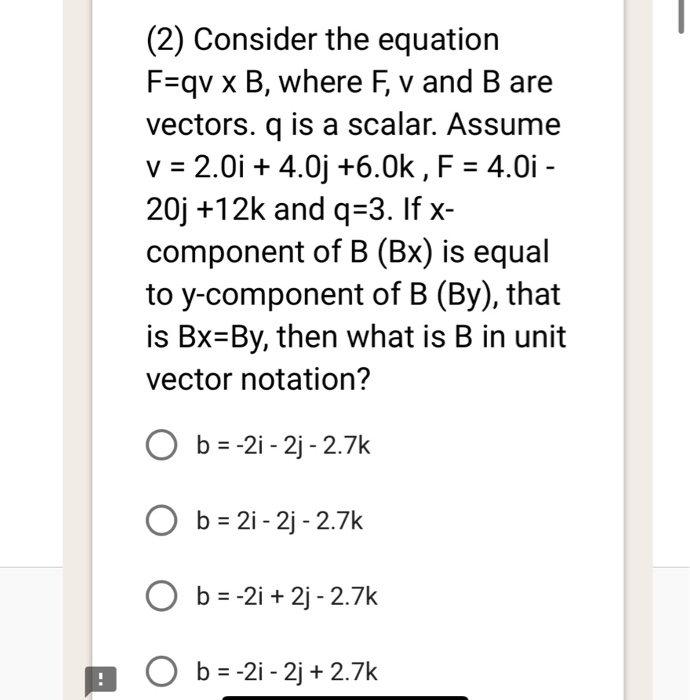



Solved 2 Consider The Equation F Qv X B Where F V And B Chegg Com




Todays Agenda Magnetic Fields You Must Understand The




Mas 119 Sn A 67 Zn B And Static 65 Cu C Nmr Spectra Of Vs And Vf Download Scientific Diagram
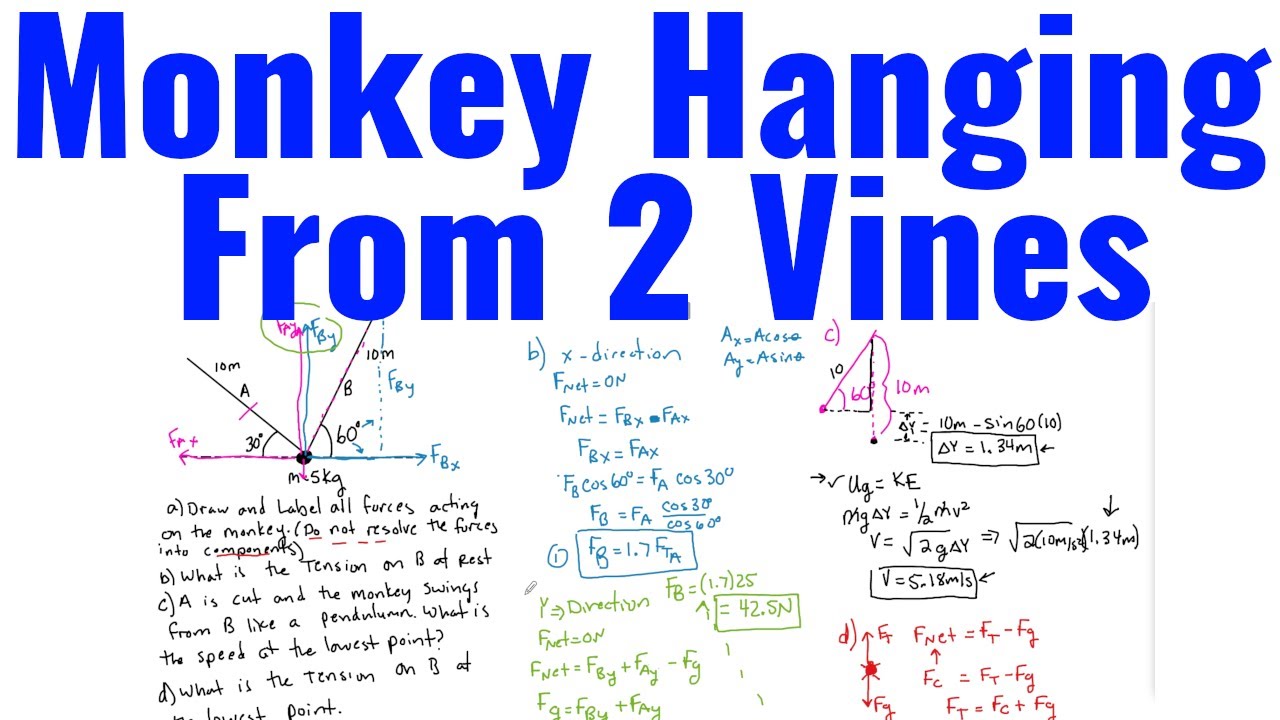



Monkey Hanging From 2 Vines Example Ap Physics 1 Youtube




Does V X Suffice To Show F In Bv A B Mathematics Stack Exchange



Running Track 3d Turbosquid



2




Don T Miss Sales On Initial Bracelets A Also In S E L U W F O K H C Y I Z Q B R X D N V T
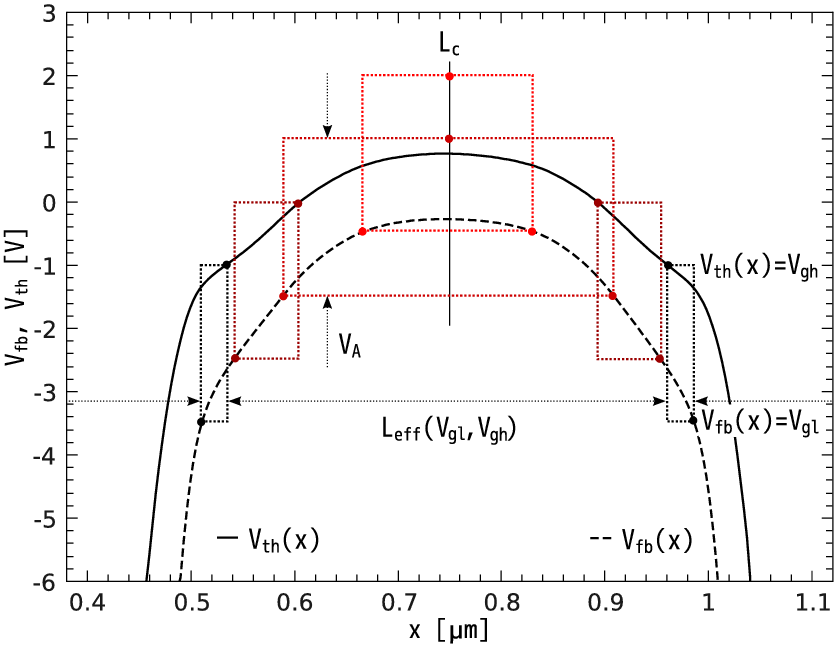



4 1 2 Effective Channel Length




Practice Problem Set 2 Riemann Stieltjes Integration



Takara Kurumada Masami Btx B T X Neo B T Vf Action Collection Figure Lavits Figure




Magnetism And Electric Currents Ppt Download



2




Misc 7 Find Derivative 1 Ax2 Bx C Chapter 13 Ncert




Solved I Let V Be A Vector Space Over F Show A B X Y Chegg Com
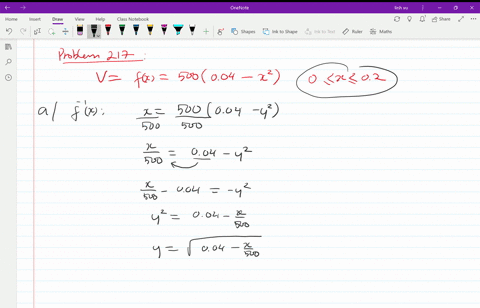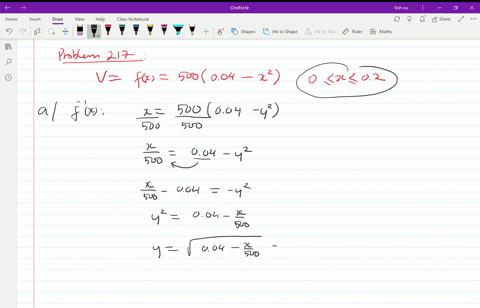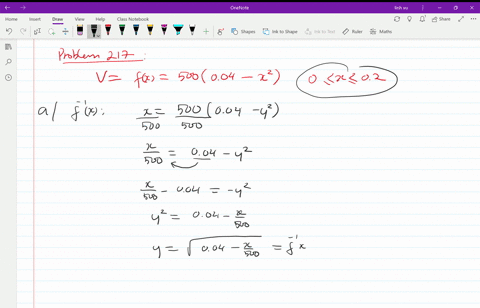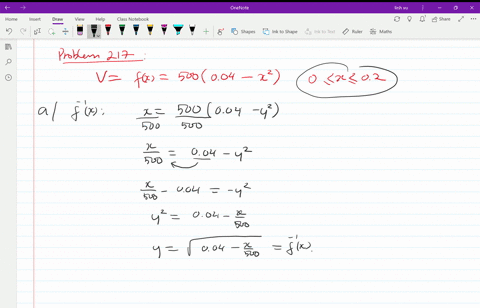



Solved T The Velocity V In Centimeters Per Second Of Blood In An Artery At A Distance X Mathrm Cm From The Center Of The Artery Can Be Modeled By The Function V F X 500 Left 0 04 X 2 Right Text



2



The Algae Algae Gt I Vv V Quot I Gt V Vo M I I Viv V Iv Quot V F Iv I Cfff I I I L Gt V B Fig 151 Trihonema A T Homhycina




Chapter 28 28 1 An Electron That Has Velocity I V 2 0 A 10 6 M




Lorentz Forces The Force F On A Charge Q Moving With Velocity V Through A Region Of Space With Electric Field E And Magnetic Field B Is Given By 11 23 Ppt Download




Observation Of A Soft Photon Signal In Excess Of Qed Expectations In Pp Interactions Topic Of Research Paper In Physical Sciences Download Scholarly Article Pdf And Read For Free On Cyberleninka




Cedar Logic Simulation Lab 1 Pdf



2




Best Mechanical Gaming Keyboard Factory Meetion




Real Analysis Lecture Notes 3 5 Functions Of Bounded Pages 1 14 Flip Pdf Download Fliphtml5



2




Ex 13 2 7 Find Derivative Of X A X B Teachoo




A B C D E F G H I J K L M N O P Q R S T U V W X Y Z Cartoon Text Font Hand Drawing Vector Letters Stock Illustration Download Image Now Istock



2
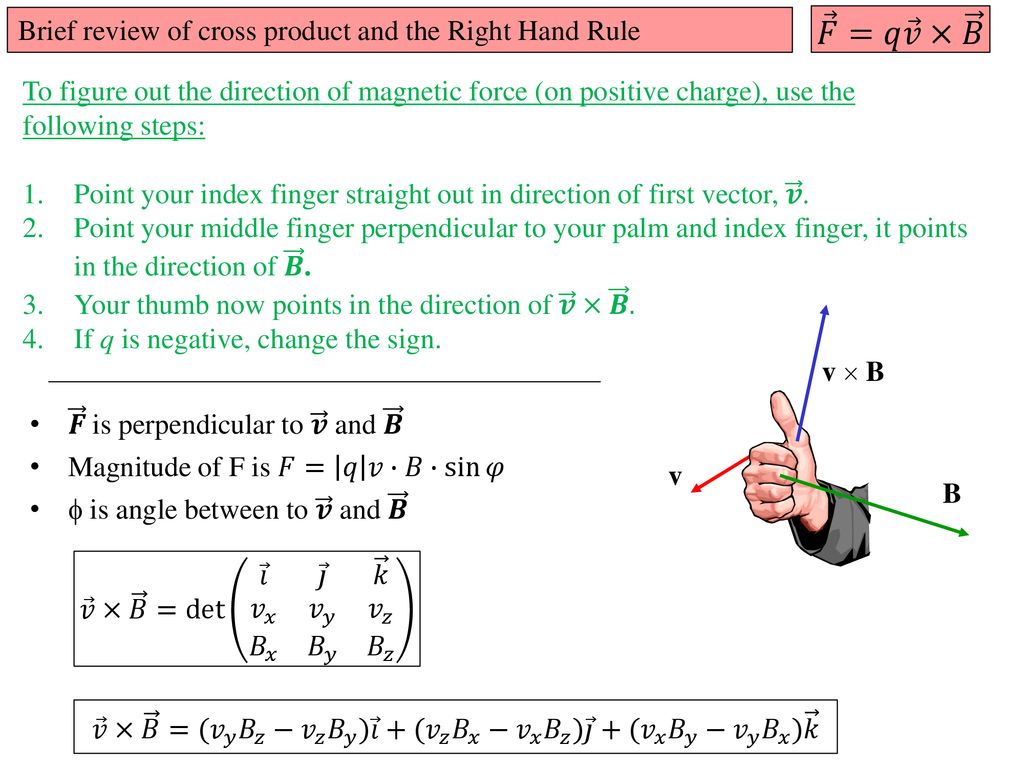



A Couple Of Announcements Unrelated To Class Ppt Download



2




3d Horten Bv 38 Turbosquid
コメント
コメントを投稿